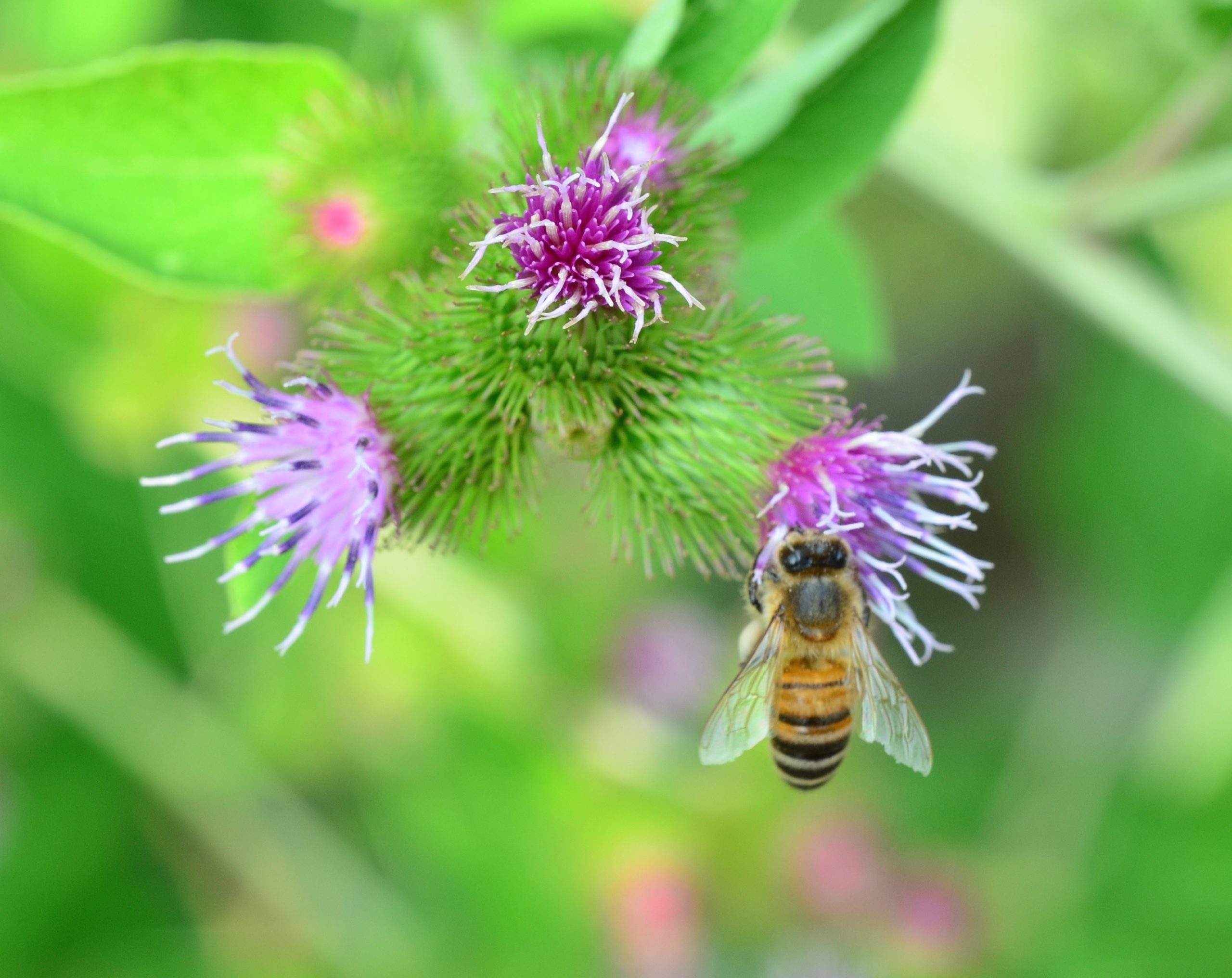
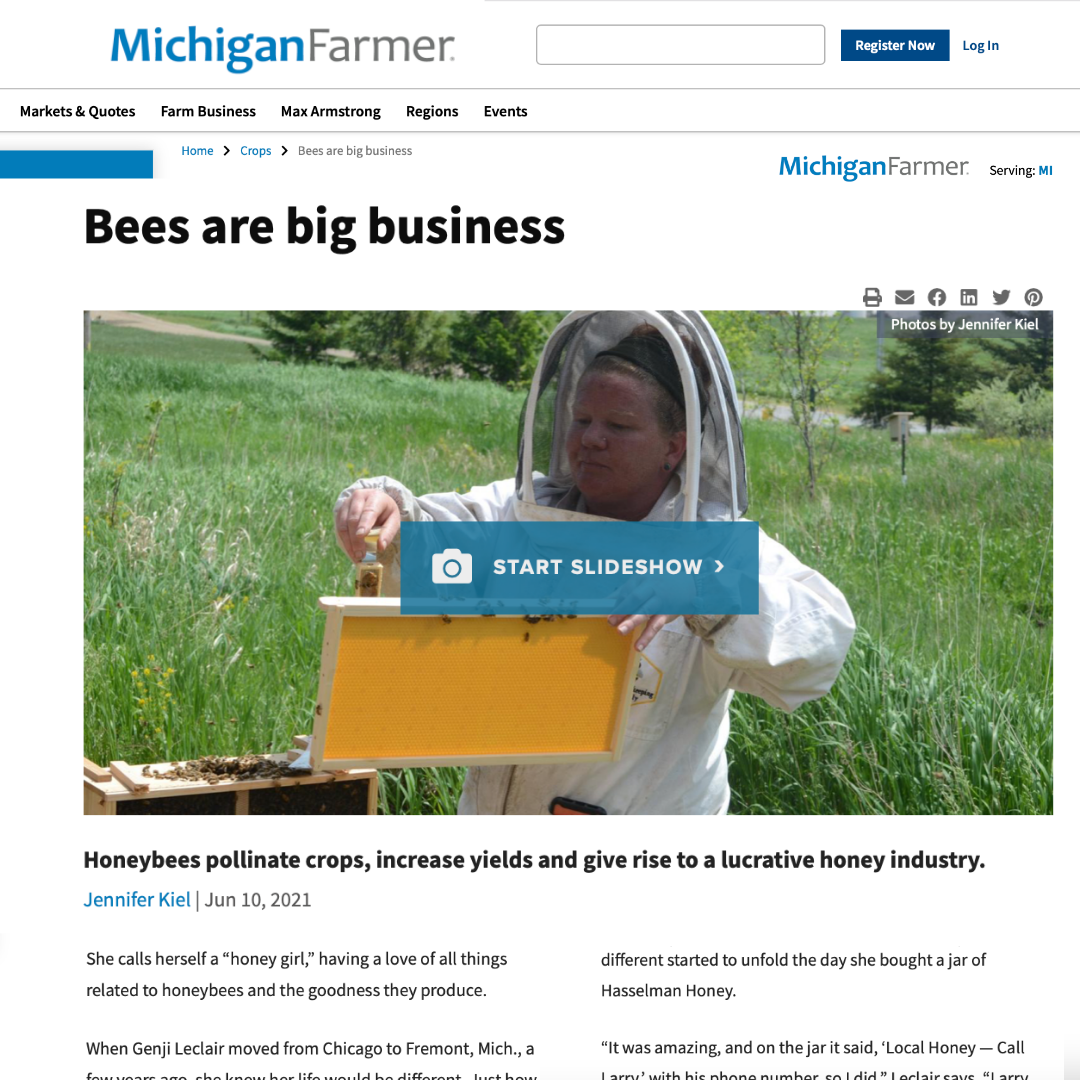
Like all living things, plants want to reproduce. Reproduction happens when a male fertilizes a female. Plants reproduce similarly by making seeds after being fertilized. In order for plants to make seeds, plants must first be pollinated. Pollination is the process by which the male part of a plant fertilizes the female part of another plant (of the same species). The male part of a plant produces pollen, which then must travel to the female part of another plant in order to fertilize it. Plants can’t pick up their feet and walk like other living animals. The male part of the plant relies on external forces to transfer the pollen to other plants, like bees.
Continue reading How Pollination Works